Several industries use 3D Printers in printing various outputs they need; The industries include footwear, architecture, jewelry, construction and engineering, education, automotive, medical and dental industries, aerospace, and consumer products.
What is a 3D Printer?
- A 3D printer is a computerized machine that allows physical object creation using a three-dimensional digital model (3D); it typically lays down thin material layers in a successive form.
- Three-dimensional printing is an additive manufacturing technique. Thus, it uses digital designs in creating physical objects.
- The process constitutes successively laying down a material's thin layers in powdered plastic or liquid form, cement or metal. Lastly, the layers are fused (Will, 2020).
How a 3D Printer works
According to Woodford (2021), inkjet printers usually spray liquid ink, while a laser printer applies solid powder in its production. Well, a 3D printer does not use any of the two. Instead, it uses plastic in physical object modeling.
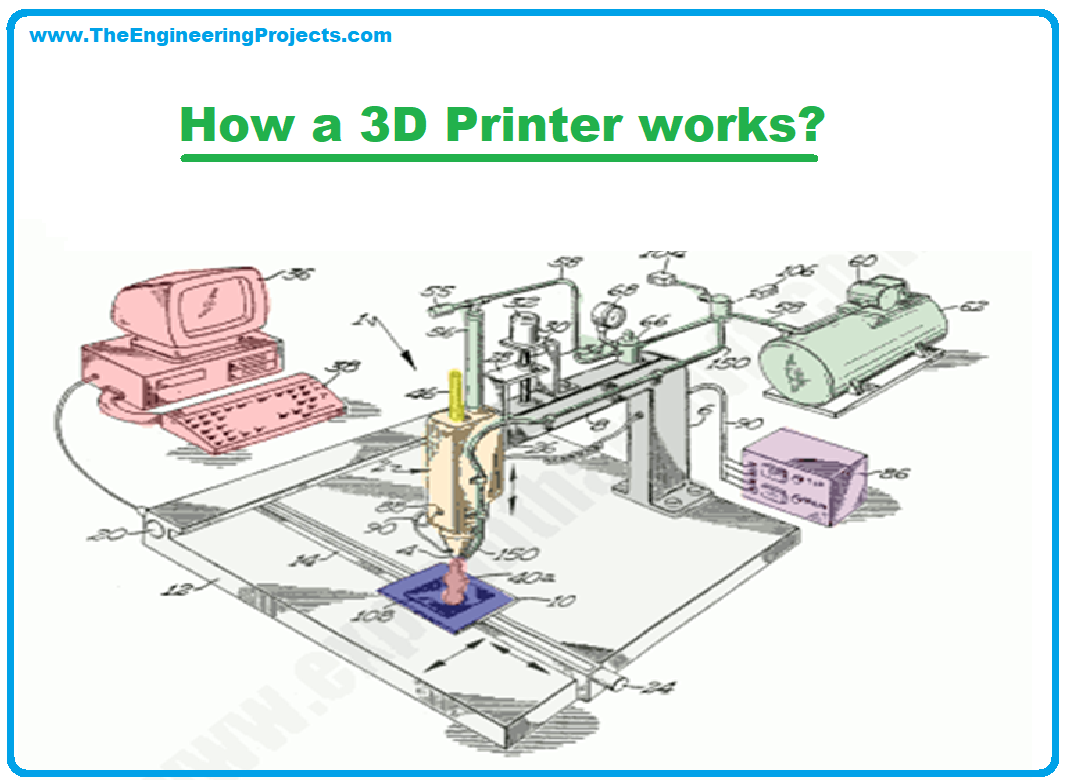
- A 3D printer functions by melting a plastic material to a molten state released via a tiny nozzle.
- The nozzle moves accordingly under computer control or automation of the 3D Printer.
- The Printer prints one layer simultaneously; a printed layer has to dry before another is published.
- The end product depends on the Printer and user skills; Mostly, the printed product is usually superb with a 3D model appearance.
- The material used in printing is equally crucial. For example, the plastic material used in the Printer will determine the quality of the object printed.
Advantages of 3D Printer
According to TWI (2021), 3D Printers in production have more benefits than traditional production methods.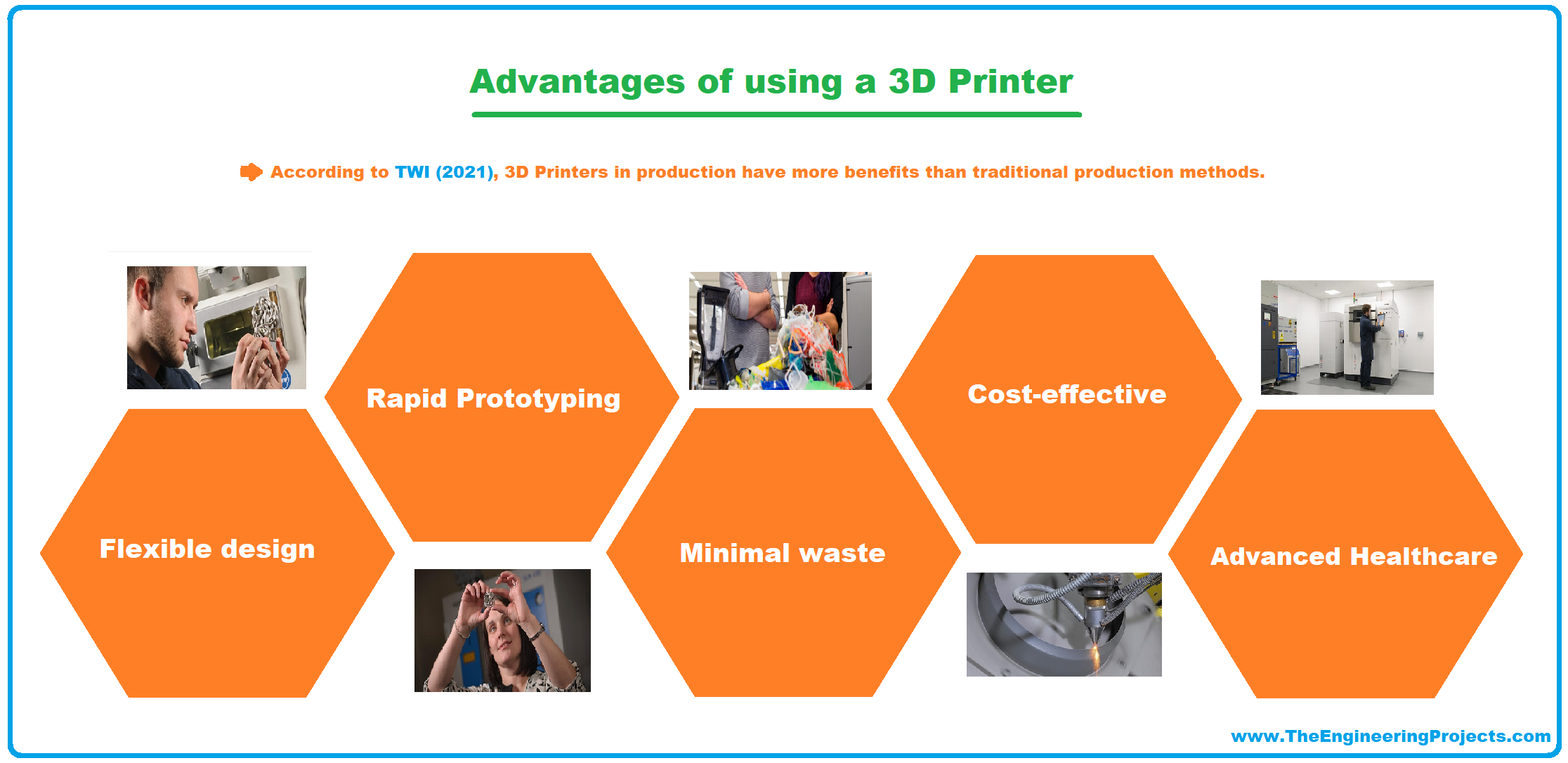
Flexible design
- 3D Printers allow the designing and printing of a variety of complex models. 3D Printers have limited restrictions in printing, unlike several traditional processes.
Printing on demand
- 3D Printers require less space in stocking inventory than the traditional processes.
- 3D Printers save costs and a lot of space because printing in bulk is not necessary unless needed.
- The 3D Printer has a virtual library where all the design files are stored.
Rapid Prototyping
- 3D Printers carry out printing very fast; they manufacture many parts within a short time.
- In comparison with machine prototypes, 3D Printers cost less and faster by allowing completion of each design model at a higher speed rate.
Solid and light parts
- Most of the material parts in 3D Printers are plastics and more minor metals.
- Therefore, plastics provide more advantages because they are lighter than metals.
- Industries such as automotive use the lightweight benefit because it gives significant fuel efficiency.
- Also, several parts are made from tailored materials, providing unique properties like higher strength, heat resistance, and water repellency.
Fast design and high production rate
- 3D Printer prints objects in a short time, i.e., an hour, depending on a part's complexity and design.
- In 3D printing, the part's manufacture provides time-saving, and design processes are extremely fast by creating ready CAD or STL files to be printed.
Minimal waste
- The parts’ production process in 3D Printer only needs the materials required for each part, with very minimum material wastage.
- In alternative methods like traditional processes, parts are cut from considerable chunks of materials, especially non-recycled materials.
Cost-effective
- A 3D Printer saves on costs in its operations; partnered with different manufacturing machines.
- The Printer can automatically work on a task if set; it does not need an operator to control its functions.
- Also, the 3D Printers reduce material cost in the manufacturing process since the process only requires the material required.
Ease of access
- A 3D Printer can quickly access more local service providers which offer outsourced services for manufacturing tasks.
- Therefore, it does not require costly transportation, unlike the traditional industrial process.
Environmental friendly
- The technology used in 3D Printers reduces wastage of materials in production processes.
- Also, the 3D Printers benefit the environmental properties like better fuel efficiency than the traditional methods.
Advanced Healthcare
- The 3D Printers are used in hospitals to save lives, especially in surgery sectors. The Printer is used in printing human body organs such as kidneys and livers.
Disadvantages of 3D Printer
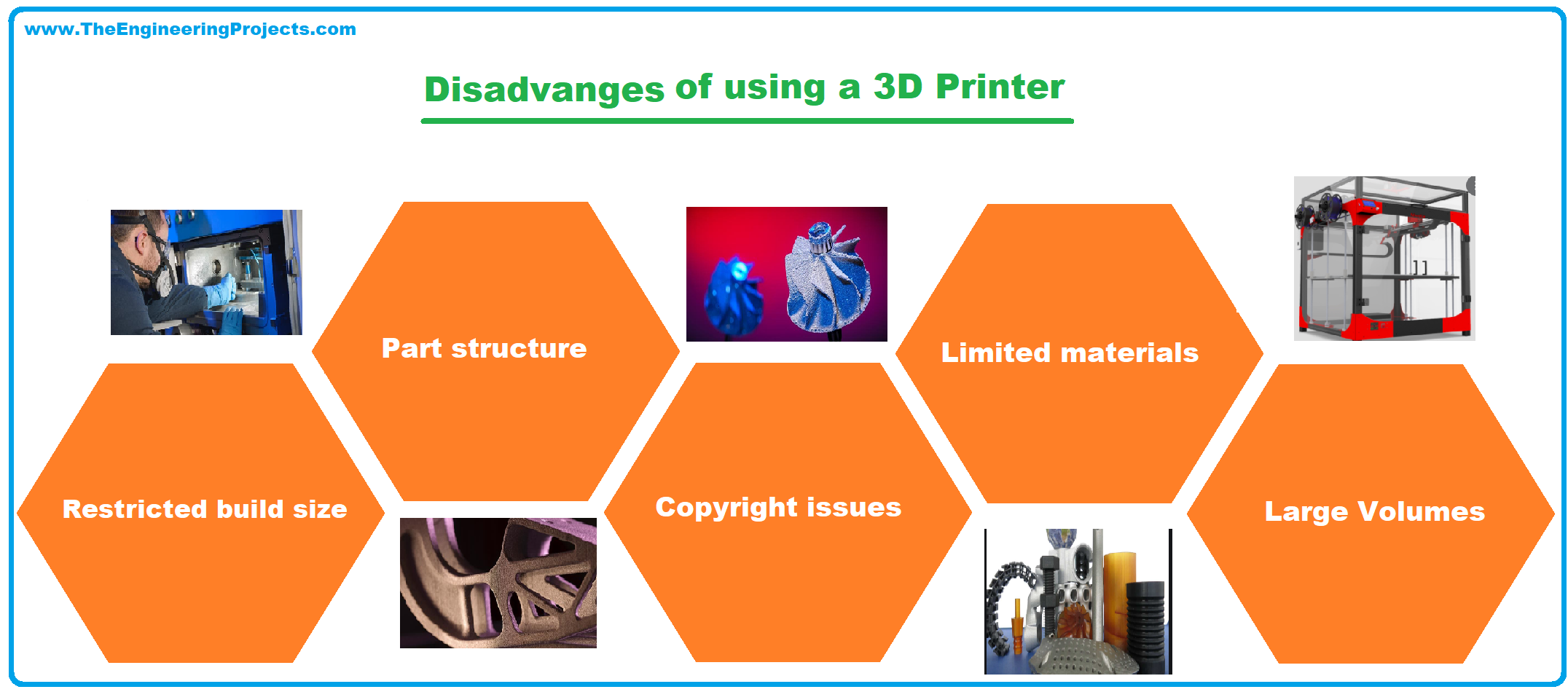
Limited materials
- A 3D Printer is limited in creating items within a selection of metals and plastics; it does not have an exhaustive raw materials selection.
- Not all plastics or metals are temperature controlled to be used in 3D Printers. Furthermore, most of the printable materials are unsafe for food and can not be recycled.
Restricted build size
- A 3D Printer’s print chambers are small. Hence the print chambers restrict the sizes of parts to print.
- Things that are larger than the print chambers are printed in parts separate from the 3D Printer.
- One can join the large and small printed objects after production, but it is much work, costs more, and consumes a lot of work.
Post-processing
- 3D printed parts require clean-up to eliminate supporting materials from the building process and create a smooth surface finishing.
Large Volumes
- The cost of 3D printing is static, unlike conventional methods such as injection molding.
- The 3D printing initial investment is lower than in some manufacturing techniques.
- But, when 3D printing is scaled for mass production of large production volumes, the cost per unit for injection molding reduces more than the 3D Printers.
Part structure
- Certain orientations or stresses can delaminate the layers because of the successive layer production in 3D printing.
- The problem commonly occurs in the production of items using fused deposition modeling (FDM). Also, multijet and polyjet are
3D Printer Models
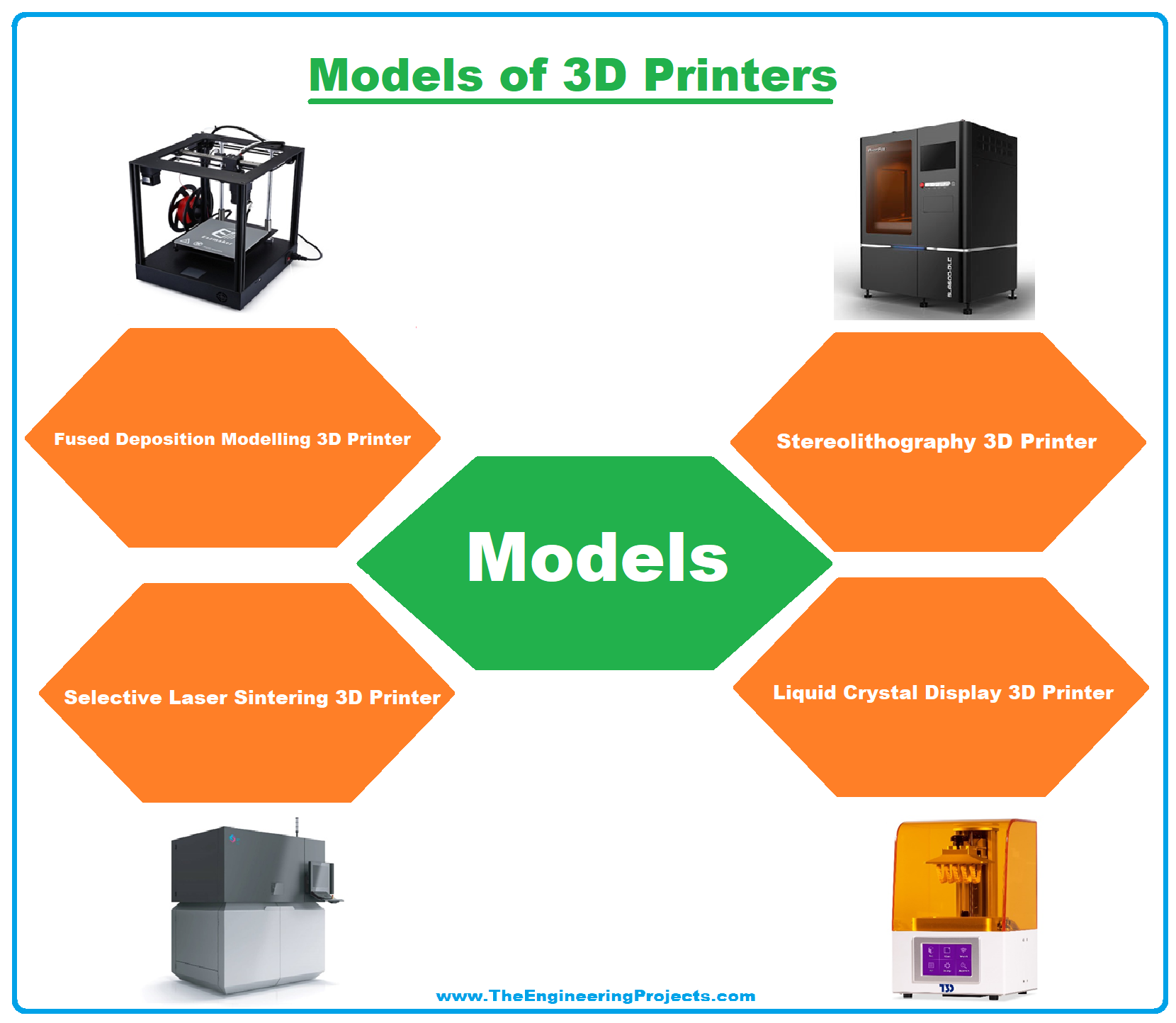
- Fused Deposition Modelling 3D Printers (FDM).
- Stereolithography 3D Printers (SLA).
- Selective Laser Sintering 3D Printers (SLS).
- Laser Crystal Display 3D Printers (LCD).
- Digital Laser Printing 3D Printers (DLP).
Stereolithography 3D Printer (SLA)
According to Formlabs (2021), the world's first 3D Printer is stereolithography, invented in the 1980s. Most professionals are still using the SLA technologies in production. The Stereolithography 3D Printer applies the photopolymerization process in its functioning; The process includes using a laser to cure liquid resin into hard plastics.
The Printer is popular because of its production ability of watertight, isotropic, and high-accuracy prototypes or parts. The parts or prototypes have advanced materials range with good quality features and smooth surface finishing. The Stereolithography resin offers vast mechanical, thermal, and optical elements to match the industrial, standard, and engineering thermoplastics properties.
Several industries use stereolithography—for example, dental, engineering, education, modeling, and manufacturing industries.
Stereolithography parts constitute a smooth surface finishing, fewer visible lines, and sharp edges.
Application of stereolithography- Concept modeling
- Dental application
- Functional Prototyping
- Rapid Prototyping
- Jewelry casting and Prototyping
- Short-run production
Liquid Crystal Display 3D Printer (LCD)
The LCD 3D Printer uses UV LCDs arrays as its light source. The LCD panels produce light that directly shines onto the building area in a parallel fashion. Pixel distortion is not a problem in LCD 3D Printer because its light is not expanded. The printing quality is dependant on the LCD 3D Printer's density; increasing the pixels produces better quality (Leo, 2019).
The LCD 3D Printer has a faster building speed when compared to SLA 3D Printer; it prints parts faster.
Selective Laser Sintering 3D Printer (SLS)
A selective laser sintering (SLS) 3D Printers sinters small polymer powder particles to form a solid structure using a high-power laser. The SLS has unfused powder whose function supports the part when the Printer is printing and removes the need for a dedicated support structure. Hence, the SLS is suitable for complex geometries, including the negative and interior features, thin walls, and undercuts (Formlabs, 2021). The SLS 3D Printer produces parts with superb mechanical characteristics. Furthermore, it has strength that resembles the injection-molded parts' strength.
The SLS’s most common material is nylon. Nylon. Nylon has suitable properties that suit the SLS 3D Printer; the properties of nylon include it is flexible, strong, lightweight, and stable against chemicals, water, impact, UV light, and dirt.
According to Formlabs (2021), The SLS 3D Printer is popular among engineers because it combines high productivity, low cost per part, and established materials. The engineers use it for functional Prototyping. Furthermore, the SLS 3D Printer is cost-effective for bridge manufacturing or limited-run.
The SLS 3D printer parts have faintly rough surface finishing and layer lines that are almost not visible.
Applications of an SLS 3D printer- End-use parts
- Functional Prototyping
- Custom manufacturing, bridge, or short-run
Fused Deposition Modelling 3D Printer (FDM)
Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM) also refers to the Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF). Consumers popularly use FDM 3D Printer. The printer functions by releasing thermoplastic filaments like the Polylactic Acid (PLA) and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) via a heated nozzle, building a platform through heating the material to melt and applying the plastic on successive layers until completion of the part (Formlabs, 2021).
The FDM 3D printer is the most favorable for simple, low-cost Prototyping and basic proof-of-concept models. Compared to SLS and SLA 3D Printers, FDM 3D Printer has the lowest accuracy and resolution; hence, it is advisable not to use the FDM 3D printers in printing designs that are complex or have intricate features. Mechanical and chemical polishing processes are used in obtaining higher-quality surface finishes. An industrial mitigates challenging issues through soluble support and allows a wide variety of engineering thermoplastics, increasing production costs.
FDM parts show visible lines responsible for creating inaccuracies when handling complex features.
Application of FDM 3D printer- Simple Prototyping
- Basic proof-of-concept models
3D Printer Resins
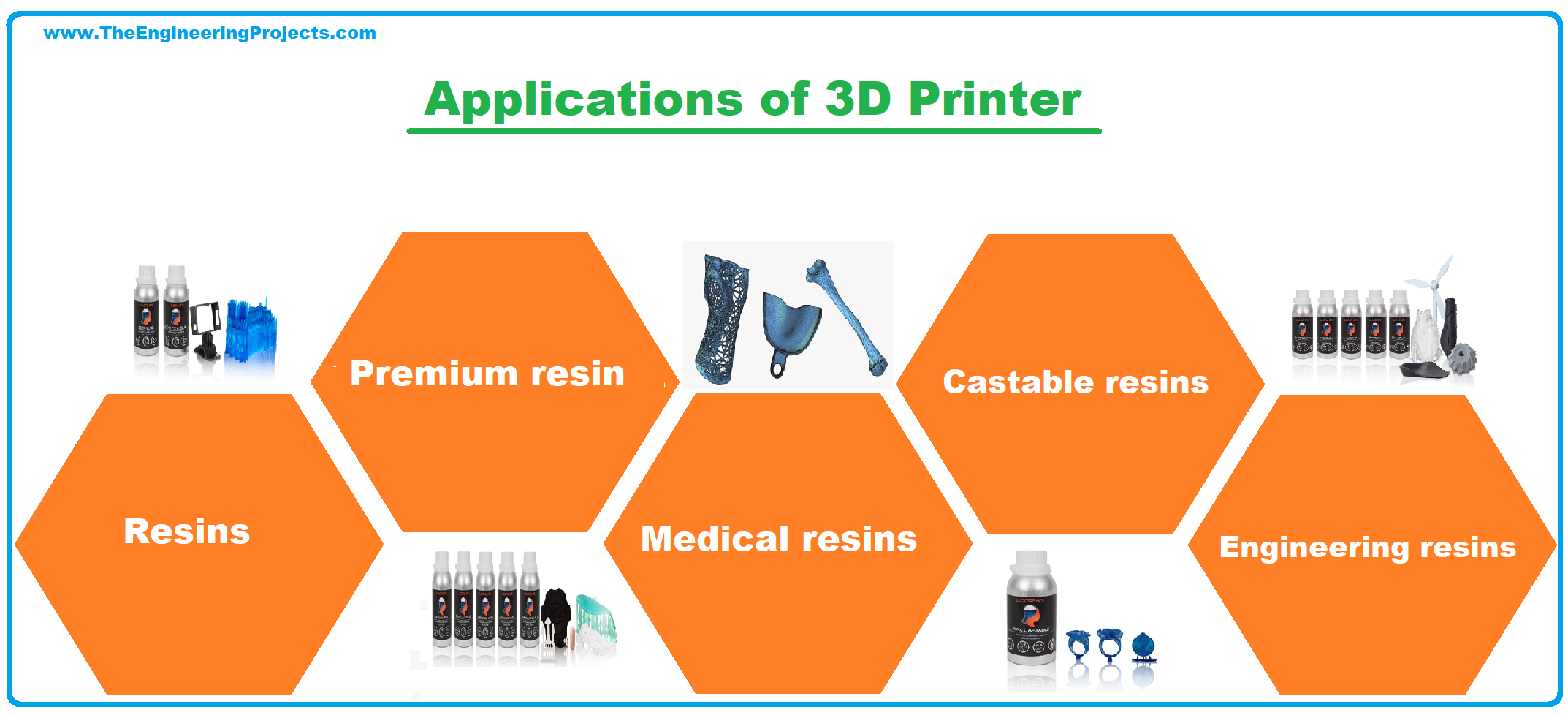
A resin refers to a highly viscous substance of synthetic or plant origin typically converted into polymers; generally, the resin is a combination of organic compounds (Liqcreate, 2021). Transparent resin is mainly used in 3D printing in a transparent material. Transparent resin is suitable for 3D printing because of its water-resistant property. Also, the transparent resin is an ideal choice for that requires high quality, smooth finish, and fine surface.
According to Liqcreate (2021), several types of resin are used in 3D Printers basing on their functions or purpose. They include the general-purpose, premium, medical, castable, engineering, and creative purpose resin.
General Purpose resins
- General-purpose resins can perform several functions and are not specifically for one task.
- The resin is ideal for a wide range of purposes in Prototyping, consumer applications, and entertainment.
- The resins have the best quality performance and costs in the market and are easy to use.
Premium resin
- Premium resins have perfect quality in LCD 3D Printers, no discoloration, and high opacity.
- The premium resin range comprises flexible and rigid resin for functional objects.
- The premium resins are suitable for in-office printing because they do not release any unpleasant odor.
Medical resins
- Each medical application has unique resin requirements—for example, dental applications or products concerning skin contact.
- Therefore, every medical operation will require a different special resin depending on the type of medical operation.
Castable resins
- Castable resin is the best in jewelry manufacturing, industrial, and dental parts.
- Castable resin is a wax-based material with a reliable casting process.
- Also, it uses a clean burnout to crisp details and provides a smooth surface finish.
- A castable resin can create custom elegant organic geometries.
Engineering resins
- The engineering resins are suitable for applications that need specific mechanical assets.
- The engineering category of resins comprises advanced photopolymers for professionals who expect tough, extreme impact resistance, and tough.
Creative resins
- The creative resin creates the 4th dimension when used in 3D printers.
- One has beautiful options when selecting the resins.
- The creative resins add feel, scent, sound, or glow to a 3D Printer.
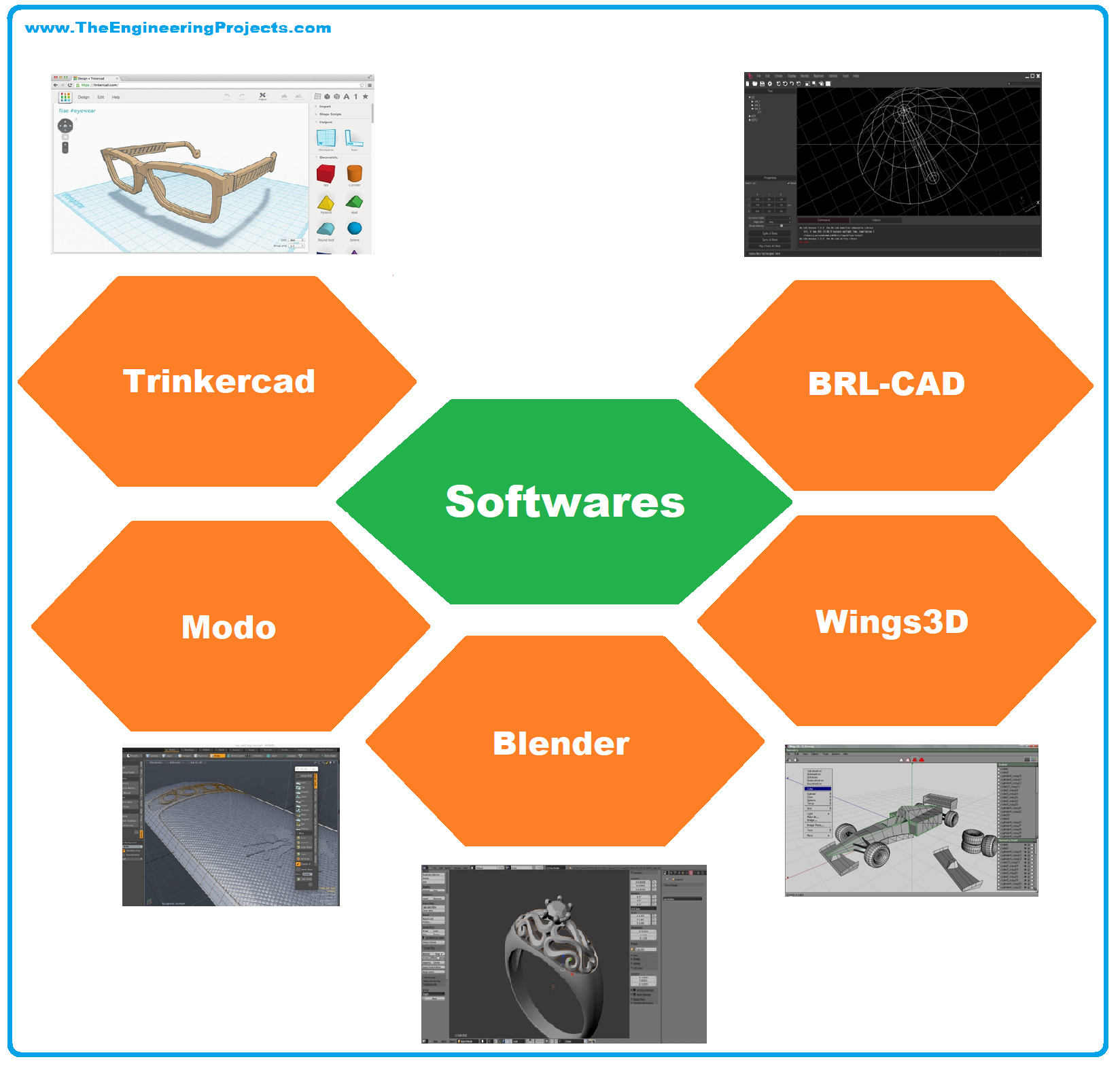
Software for 3D Printing
In the past, people used a lot of resources to study Software about modeling software. Some software is easy to use, and some are free to access. Some software use solid modeling whereby they produce manifold models. While other Software is watertight, a manifold model refers to a model with some thickness in all of its walls (Strikwerda, 2021). Softwares that use polygon modeling create walls with zero thickenings; such walls are suitable for creating graphics for movies and games contrasting with 3D printing. The polygon modeling software makes the manifold models, but it would need a lengthy procedure and more experience. The Software listed in the article generates 3D printable models. Some of the Software is easy to use. At the same time, others are more suitable for professionals rather than for amateurs.
Trinkercad
According to Strikwerda (2021), Trinkercad software is a browser-based app and freely available to all users, and it applies solid modeling in its work. The creation of the Software targets beginners. Trinkercard software is unique because it introduces solid modeling and allows any person to make 3D printable modeling.
The Software applies the block-building concept. Therefore, it allows one to create models from a variety of basic shapes. The Software also provides aid to beginners through its guides and tutorials. Furthermore, the Software has the advantage of exporting or sharing with ease.
Trinkercad has an extensive library that constitutes millions of files that give the users several distinct options for finding the best shapes that will suit their problem requirements best. The Software allows the user to print and have the product instantly at your location through direct integration with other printing services. It is the best platform to learn about 3D modeling and printing.
Blender
According to Strikwerda (2021), Blender software is freely accessible to its users. The Software is not a solid model; it is open-source, rich in features, and constitutes animation, rendering, sculpting, video editing, simulation, and motion tracking. Also, the Software is very friendly since both advanced users and amateurs can use it.
The Blender Software constitutes many 3D creation facets, including simulation, animation, and modeling, e.t.c. The software suits individuals who are ready for transitioning from learning to designing complex 3D models.
One of Blender's exciting features is the photorealistic rendering feature. The feature creates models to reality; only a few free software can have such a feature.
BRL-CAD
According to Strikwerda (2021), the BRL-CAD Software is a type of Open-source Software. Also, it is an advanced solid model system comprising interactive geometry editing. The U.S military uses the BRL-CAD Software in modeling weapons and related systems. This shows the Software is very advanced and quite dependable. The Software serves its users with a precision of high level by using specific coordinates in arranging the geometric shapes.
The Software provides complex and simple shapes to its users to make their designs, having an extensive library of files. The Software allows combining multiple different forms to generate the desired model. BRL-CAD Software performs its tasks fast due to its dense features. Furthermore, it is free and available for access to all users.
Wings3D
According to Strikwerda (2021), Wings3D is an open-source software type; polygon modeling tool and has a broad range of selection and mesh tools regardless of its freeware. The Software is user-friendly, with beginners as the primary target; it has a steady learning curve. Its features, such as the easy-to-use interface and customizable hotkeys, indicate the designing or printing status; hence, the Software suits the starters.
The Software has no shortage of valuable or essential features like the inset or plane cut; thus, it can create impressive models. Moreover, the Software supports a vast range of both import or export file formats.
Modo
According to Strikwerda (2021), Modo 3D Printer software creates a creative 3D polygon modeling tool. Also, it can provide a subdivided surface designing tool that has more flexibilities for creating both the precision meshes and freeform organic designs through the use of the same Software. The Software is strictly used by professionals or advanced 3D printing users. The Software is not user-friendly, and it is costly to operate.
Modo has a wide variety of features and runs its processes smoothly. It has a very high speed in production and modeling. The Software allows extensions of partnering with other Software in production activities.
Price of a 3D Printer
The price of a 3D printer varies based on the type of printer and the needs of the user. If you rank all of the many 3D printers on the market, you'll come up with a price of $400. However, as of April 2021, the price has dropped to $ 200-$500, with some being quite pricey at $ 1500. Professional 3D printers and enthusiast 3D printers, for example, range in price from $ 1,500 to $6,000, depending on the printing capability. Finally, industrial 3D printers are expensive to buy and operate, ranging from $20,000 to $100,000.
So, that was all for today. I hope you have enjoyed today's lecture. If you have any questions, please ask in the comments. Take care.


 3D Printing
3D Printing richarddavis
richarddavis 0 Comments
0 Comments


















 2.3k
2.3k
 953
953
 921
921
 2.1K
2.1K

