High-voltage power systems form the backbone of advanced electrical energy generation, transmission, and allocation. As voltage levels rise to hundreds of kilovolts in communication networks, the direct measurement of voltage becomes both unsafe and unusable. Standard measuring tools, such as voltmeters, relays, and meters, are designed to operate at moderate voltages and cannot be connected directly to high-voltage cables. This problem is addressed using Potential Transformers, also known as Voltage Transformers.
Potential transformers play a crucial role in high-voltage measurement by stepping down high voltages to secure, interchangeable values while maintaining accuracy and delivering electrical isolation. What is a potential transformer? It is a device that steps down high voltage to a safe, balanced level, allowing precise measurement and safety in high-voltage systems.

1. Introduction to Potential Transformers:
A potential transformer is a specialized tool transformer designed to measure high voltages indirectly. It converts a high primary voltage to a lower secondary voltage that can be safely measured by traditional tools. The modification is accomplished in a precise ratio, provided that the secondary voltage properly illustrates the primary voltage under normal operating situations.
- Providing accurate voltage information for metering and protection
- Enabling standard low-voltage instruments to be used in high-voltage systems
- Reducing high system voltage to a low, measurable value
- Ensuring operator and equipment safety through isolation
In high-voltage systems, potential transformers are important for monitoring system voltage, handling power flow, allowing protective relays to function perfectly, and providing proper energy metering. Without PTs, reliable voltage measurement and system security at high voltage levels would not be feasible.
Expert’s Insight:
“Potential transformers play a vital role in facilitating the measurement of elevated voltage levels using conventional voltage meters and various testing apparatus.”

2. Need for Potential Transformers in High-Voltage Measurement:
Direct measurement of high voltage poses several severe challenges. Foremost, the insulation conditions for instruments capable of directly controlling high voltages would be excessively complicated and pricey. In high-voltage systems, potential transformers are necessary for monitoring system voltage, handling power flow, permitting protective relays to function correctly, and supplying proper energy metering.
- Poor accuracy due to leakage and electromagnetic interference
- Extremely high insulation requirements for instruments
- Increased chances of equipment damage
Potential transformers overwhelm these challenges by decreasing high voltage to a standardized low voltage, generally 110 V, 100 V, or 63.5 V, relying on system measures. This permits the use of common measuring instruments while providing operator safety and system dependability.
| Importance of Potential Transformers in High-Voltage Systems | |
|---|---|
| Aspect | Importance of High-Voltage Measurement |
| Instrument protection | Shield matthers and relay from storage surges |
| Power System Reliability | Improves fault response and system stability |
| High-voltage compatibility | Make a low-voltage instrument usable in HV systems |
| Operator safety | Prevents direct contact with high-voltage lines |
| Measurement accuracy | Ensures reliable voltage data from billing and analysis |
| Energy billing | Enables the correct calculation of power and energy |
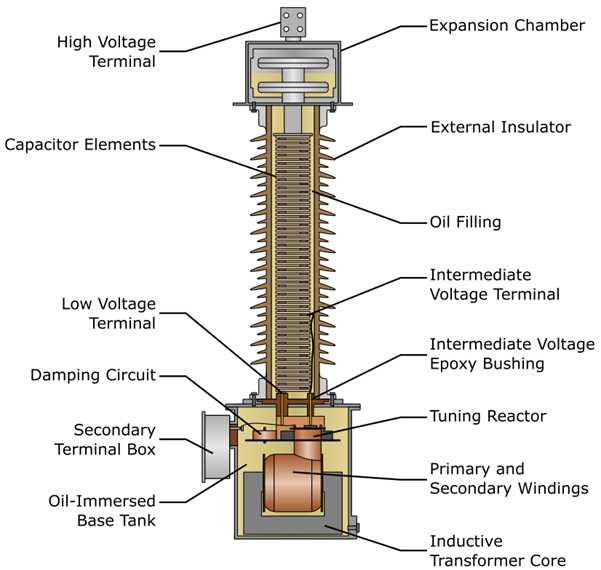
3. Construction of Potential Transformers:
The construction of a potential transformer is identical to that of a traditional power transformer, but with detailed design reviews to ensure precision and protection. It consists of a laminated magnetic core made of high-quality silicon steel to decrease core losses. The primary winding is connected to the high-voltage cable and is developed with a large number of turns and insulation to withstand high voltage stress. The secondary winding has fewer turns and supplies a low, standardized voltage.
Main components:
Magnetic core:
- Minimizes hysteresis and eddy current losses
- Made of high-grade silicon steel
Primary winding:
- Has a large number of turns
- Designed with strong insulation to withstand high voltage
- Connected to the high-voltage cable
Secondary winding:
- Supplies, measuring instruments, and relays
- Provides low output voltage
Insulation system:
- Ensures safe operation under high electrical stress
- Uses oil, resin, or gas depending on the voltage level
The design also minimizes leakage flux and magnetic saturation, which could otherwise present measurement mistakes.
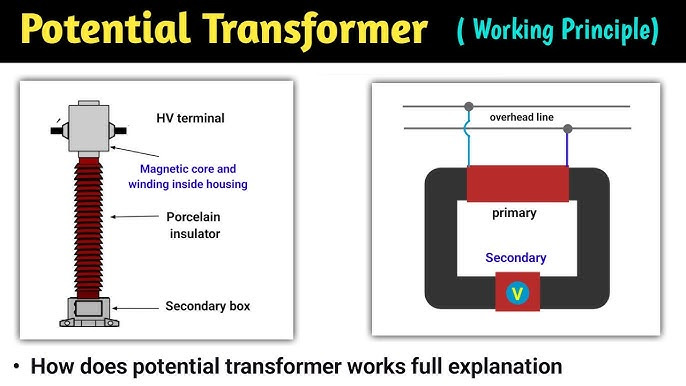
4. Working Principle of Potential Transformers:
The function of a potential transformer is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When an alternating voltage is applied to the primary winding, it makes an alternating magnetic flux in the core.
- An alternating magnetic flux is produced in the core
- A proportional voltage is induced in the secondary winding
- An AC voltage is applied to the primary winding
- This flux links both primary and secondary windings
The proportion of the primary voltage to the secondary voltage is similar to the ratio of the number of turns in the primary winding to that in the secondary winding. This general ratio permits the authentic high voltage to be calculated by estimating the secondary voltage. Since the secondary side works at a low voltage, it is safe to link measuring tools and protective devices.
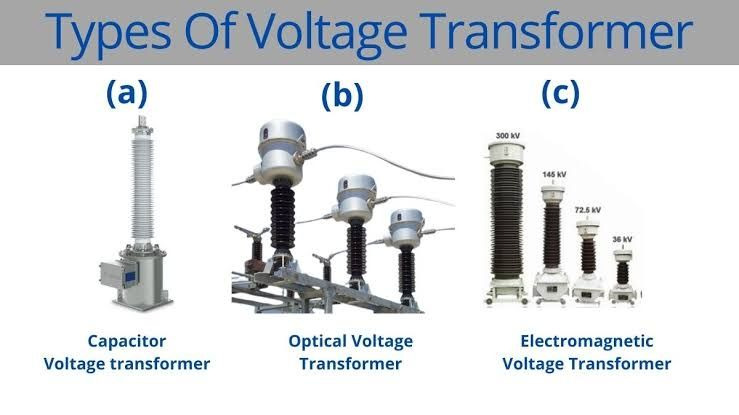
Types of Potential Transformers:
Potential transformers are categorized based on structure, insulation, and application.
1. Electromagnetic Potential Transformers:
Electromagnetic potential transformers are the most standard type and work on the same principle as conventional transformers. They are widely utilized in low to medium-high-voltage systems.
2. Capacitive Voltage Transformers:
Capacitive voltage transformers are operated in very high-voltage systems, generally above 132 kV. They operate a series of capacitors to split the voltage before applying it to an electromagnetic transformer. CVTs are more economical and compact for extra-high-voltage applications and are typically used in transmission substations.
3. Indoor and Outdoor Potential Transformers:
Indoor and outdoor potential transformers are categorized based on installation environment. Indoor PTs are used in switchgear panels, while outdoor PTs are organized to withstand environmental requirements such as temperature variations, moisture, and pollution.
5. Accuracy Conditions and Errors in Potential Transformers:
Accuracy is a crucial condition for potential transformers, particularly in metering and protection applications. PTs are designed to hold a precise voltage ratio and minimal phase angle error between primary and secondary voltages.
Types of errors:
- Ratio error: Difference between actual and nominal voltage ratio
- Phase angle error: Angular difference between primary and secondary voltage
To handle these errors, PTs are fabricated according to international standards and categorized into exactness classes. Metering PTs need very high accuracy, while protection PTs prioritize dedicated performance under abnormal circumstances, such as faults and voltage surges.
6. Role of Potential Transformers in Metering:
One of the most important roles of potential transformers is in electrical energy metering. Authentic voltage measurement is important for calculating power and energy consumption. PTs provide scaled-down voltage signals to energy meters, confirming precise billing and system monitoring.
Metering applications:
- Voltmeter
- Power and reactive power measurement
- Energy meters
In a high-voltage transformer station, PTs work in conjunction with current transformers to provide voltage and current signals to wattmeters, varmeters, and energy meters.
7. Role of Potential Transformers in Protection Systems:
Potential transformers are crucial elements of protective relaying systems. Protective relays depend on precise voltage information to notice abnormal conditions such as overvoltage, undervoltage, phase imbalance, and system faults. PTs supply these voltage signals in a safe and isolated form.
Protection functions supported by PTs:
- Undervoltage protection
- Distance protection
- Overvoltage protection
- Directional protection
During faults, voltage levels can oscillate, especially. Protection-class PTs are organized to withstand these circumstances without saturation or damage, provided that protective relays obtain reliable input signals and can work fast to isolate faulty sections of the power system.
8. Safety and Electrical Isolation:
One of the most important contributions of potential transformers is protection. By providing electrical isolation between high-voltage circuits and low-voltage measuring devices, PTs protect operators, keeping personnel and equipment from unsafe voltage levels.
How PTs improve safety:
- Protect operators from accidental contact with live conductors
- Shield measuring instruments from voltage surges and transients
- Provide whole electrical isolation between high-voltage and low-voltage circuits
Safety benefits:
- Improved reliability of measuring equipment
- Enhanced protection for maintenance personnel
- Reduced risk of electric shock
9. Role in System Monitoring and Control:
Potential transformers help with ongoing monitoring of voltage levels across the power system. Automatic voltage controllers and control systems depend on proper PT signals to keep voltage within permitted limitations.
Applications include:
- Load balancing
- Power system control
- Voltage regulation
In advanced power grids, PTs also sustain digital monitoring systems, supervisory management, and data acquisition systems.
10. Advantages of Using Potential Transformers:
Potential transformers suggest several benefits in high-voltage measurement. They deliver precise and dedicated voltage scaling, providing precise measurements. They improve security by isolating high-voltage circuits from measuring instruments.
Key advantages:
- High level of safety and isolation
- Long service life
- Accurate voltage scaling
- Reliable operation under harsh conditions
- Compatibility with standard instruments
11. Limitations of Potential Transformers:
Despite their benefits, potential transformers have specific regulations. They are subject to mistakes due to core losses, winding opposition, and temperature variations. At very high voltages, electromagnetic PTs become unwieldy and expensive, leading to the adoption of capacitive voltage transformers.
- Bulky size at very high voltages
- Higher cost compared to low-voltage measurement
- Measurement errors due to core losses
12. Importance of Standards and Testing:
Potential transformers are fabricated and tested according to international measures to provide precision, safety, and dependability. These standards describe exactness classes, insulation levels, testing methods, and performance conditions. Routine testing, including ratio tests, insulation resistance tests, and accuracy assurance, confirms that PTs perform as intended throughout their assistance life. Compliance with measures is crucial for maintaining system integrity and conviction in measurement outcomes.
Conclusion:
Potential transformers play an essential part in high-voltage measurement by allowing authentic, safe, and dedicated voltage monitoring in power systems. They change high voltages into standardized low values that can be measured using traditional tools, while providing critical electrical isolation. Their significance grows beyond measurement to security, metering, system management, and safety. In advanced power networks, where reliability, accuracy, and safety are paramount, potential transformers are essential features. Whether utilized in energy metering, protective relaying, or system monitoring, PTs guarantee that high-voltage systems operate effectively and securely. As power systems continue to develop and voltage levels expand, the role of potential transformers in high-voltage measurement will remain vital and imperative.



 Electrical Projects
Electrical Projects xeohacker
xeohacker 0 Comments
0 Comments


















 2.3k
2.3k
 953
953
 921
921
 2.1K
2.1K

