Hello, students here in our previous tutorial we study molecules and now I am with a new topic “Ion” which might be possible for some of my readers this article seems to be new, and some of my readers may be familiar with this term. But no matter whether we know or not, in my article I try to cover all aspects of this term. Many questions arise in your mind such as you may think;
What is an ion?
How ions are formed?
What are the different types of an ion?
What methodology is utilized for assigning charge to an ion?
What are examples of an ion?
Which methods are used for the creation of an ion?
If my readers want to know the answers to these questions, hold copies and pencils in your hand and stick to my article till the end.
Brief description of an Ion
What is an ion?
Definition
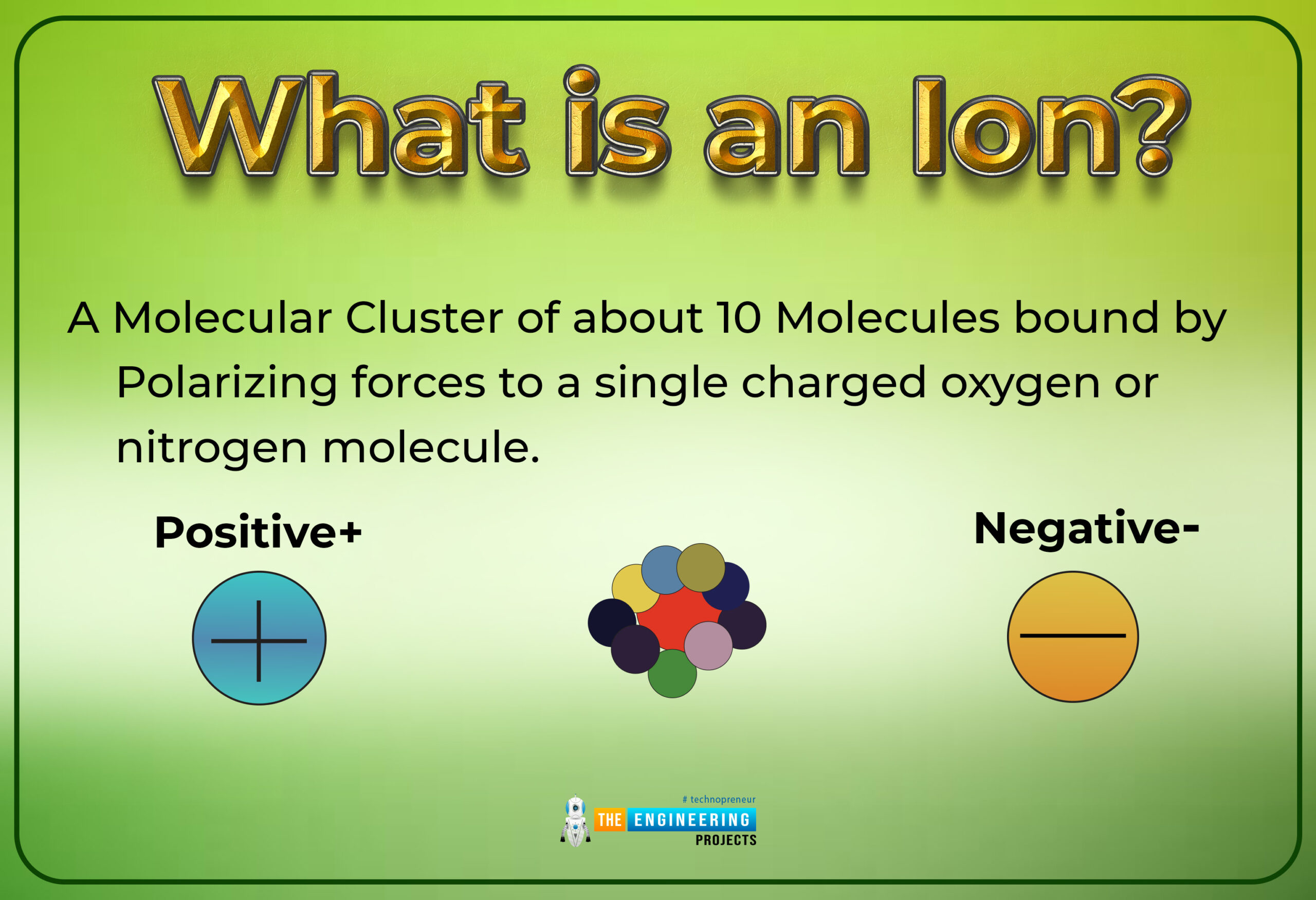
An atom or group of atoms that brings a positive or negative electric charge as a conclusion of including lost or achieved one or more electrons
Or
A charged subatomic particle (such as a free electron)
By the word an Ion, it's not wrong to say that it is the type of chemical species which may hold two types of charges with some magnitude. These charges may be positive or negative with some magnitude. Those atoms or molecules that have unequal net charges associated with them simply say that charges on them are not involved in a factor of zeros, we use the term an ion for such types of atoms.
A short view over term atom.
Atom
As this term is the basis of chemistry everyone is familiar with this term. For understanding the article in a better way I explain it. Atom is the smallest component that constitutes the property of an element. An atom has a heavy central Part which is known as the nucleus. In the nucleus, two types of charges are present one is a proton carrying a positive charge and the other is a neutron neutral particle. Overall there is a positive charge in the nucleus. Around the nucleus, there are several circular orbits in which electrons keep moving the nucleus. In each orbit, electrons feel a nuclear pull that restricts their motion in a circular orbit.
Back to our statement that ions have a non-zero net charge. By non-zero net charges, it concluded that may an atom have more protons ( sub particle of an atom that consists of a positive charge. These charges are present inside a nucleus) than several electrons ( sub particle of an atom constituting a negative charge and present outside the nucleus, keep in motion in orbits around the nucleus) or secondly, maybe there are a greater number of electrons than the number of protons in their atomic or molecular structure. Thus we can say that a charged atom or molecule is named an ion. It is charged because we see that the number of protons and electrons is unequal.
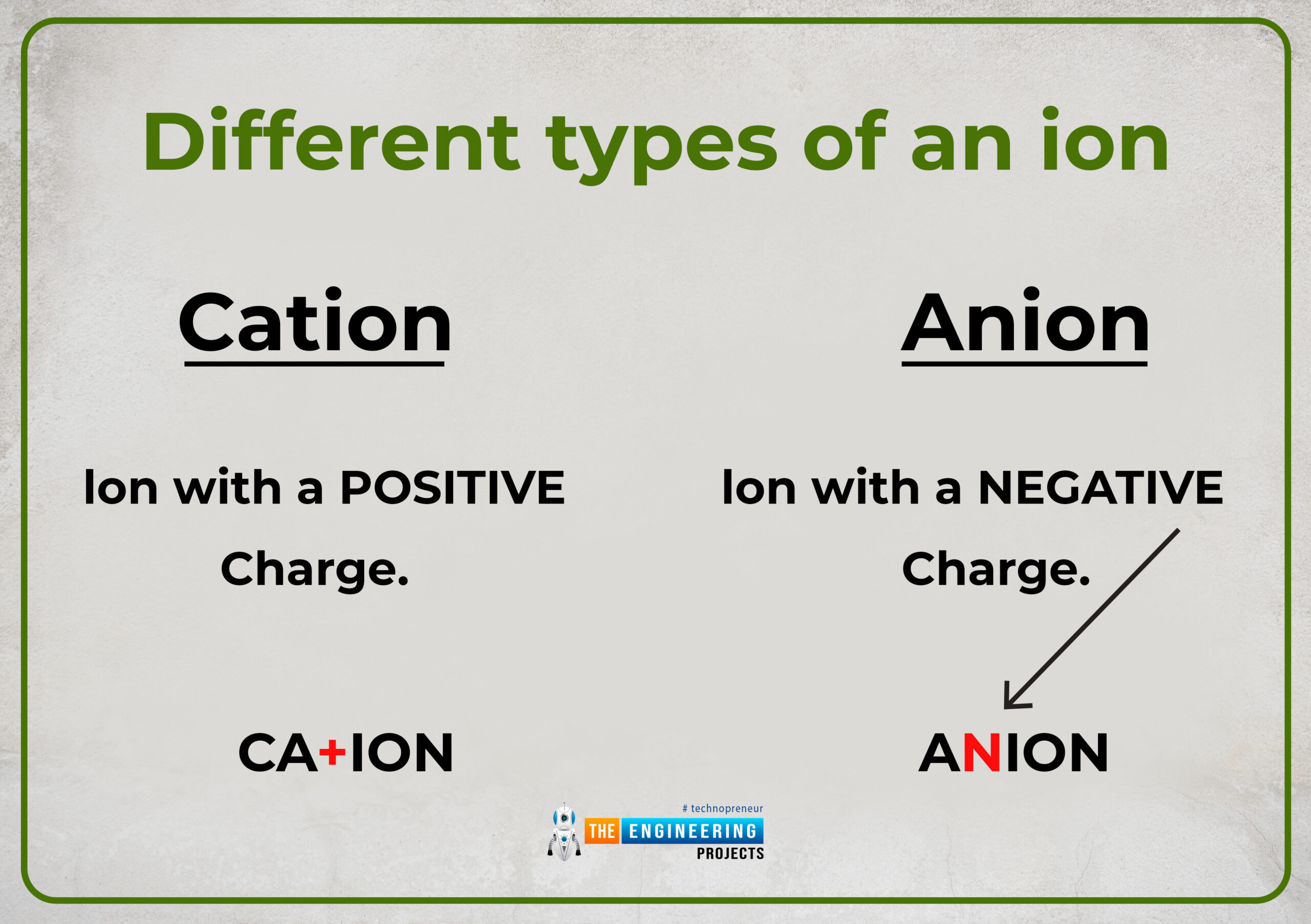
Different types of an ion
Two conditions of inequality of charges between sub-particles of an atom are mentioned. Depending upon these two conditions we can categorize an ion into two different types either positive ion (cation) or negative ion(Anion).
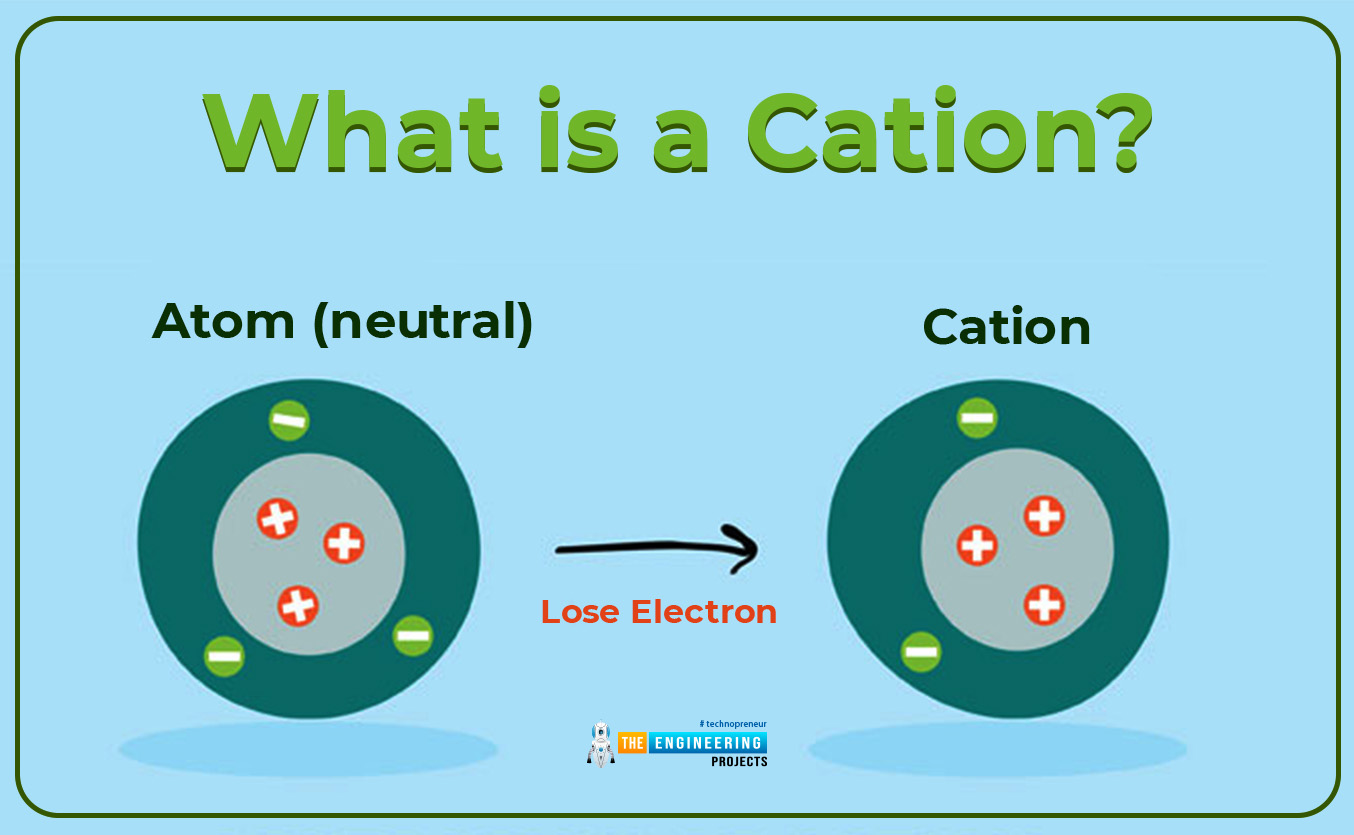
What is a cation?
According to the first condition, when the number of protons is greater than the number of the electron in an atom, then the atomic structure is knowns to be positively charged. Such positively charged atoms are known as cations or positively charged ions. The charge on a cation depends upon the tendency of an atom to lose electrons from the shell. If one electron is removed then the charge is +1, if two electrons are removed from the shell then the cationic charge is +2 as illustrated in the given below example.
- It has been seen that the formation of cation is an endothermic reaction.
What does mean by term Endothermic?
The word endothermic means heat absorbing. Endothermic reactions or processes are those in which there is a need for absorption of heat to carry out the reaction.
Why it is an endothermic reaction let’s allow me to explain:
- Cation is formed when an isolated atom loses one or more electrons from its valance shell. As we know that there is the existence of a strong force of attraction in an atom. Due to this force of attraction nucleus strongly attract the valance electron, to remove an electron from a strong grip of the nucleus a sufficient amount of energy is required. This sufficient amount of energy is given to the electron which energies it and helps it to kick off from the strong field of the nucleus. As soon as the electron removes from the nucleus field it left behind a positive charge. Which is named cation. That’s why the formation of cations is an endothermic process.
Ionization energy:
The amount of energy that is required to pull out an electron from the valance shell of an atom is named ionization energy. An example is given below to illustrate the above statement:
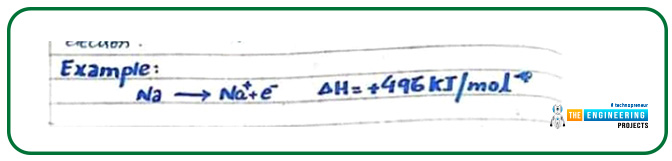
Here 496 KJ/mole energy is required to form positive cation sodium from an isolated sodium atom.
- If we compare a cation with a parent atom by their size we concluded that A Cation is smaller than the parent atom. Why does this so happen?
When a positive cation is formed then the number of protons increases as compared to the number of electrons. As one or more electron are removed from the valance shell, there is the removal of the shell from an atom result in an increase in the nuclear pull on the remaining valance electron. That’s why the cation is less than the parent atom by its size.
How does a cation Represent symbolically and what charge does it constitute?
- It possesses a positive charge and suffix (ium) is used for cation. Such as Hydronium (H+)
What is Anion?
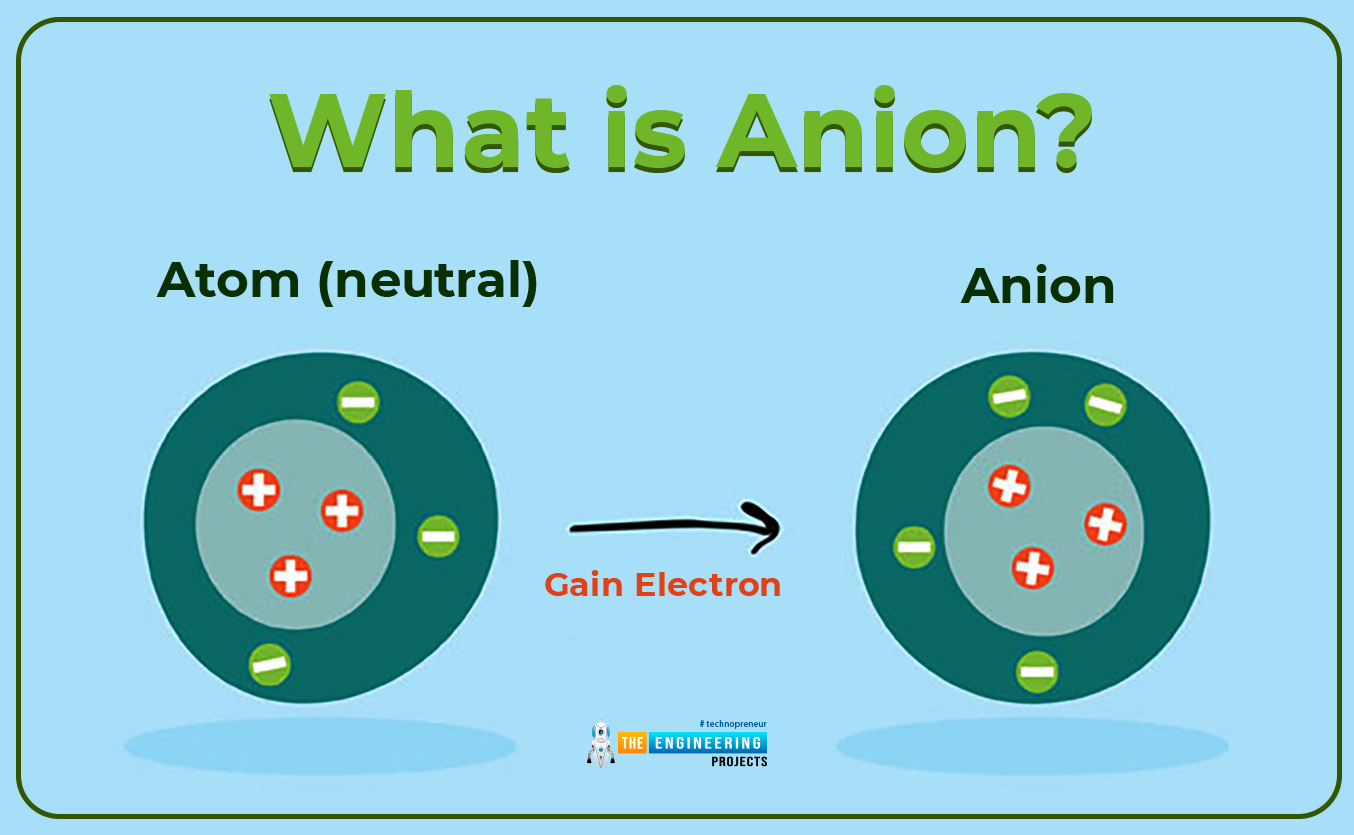
- Secondly when an atom has more electrons than the number of protons then the charged atom is referred to as an Anion or negatively charged ion. In other words, we can also say that an anion is formed when an isolated atom gains an electron.
- It has been seen that the formation of anion is an exothermic process.
What is meant by the word Exothermic?
An exothermic process is a process that occurs with the liberation of heat or energy. An anion or negatively charged ion is formed when an extra electron is gained by an isolated atom, this addition of extra electrons increases the energy of the atom resulting in instability of an atom. To attain stability, as the atom earlier it loses energy in form of heat. Thus the formation of uni-negatively ion is an exothermic process. Given below there is an example mentioned to explain the above statement:

Here when an electron is added to an isolated atom of chlorine, an amount of energy 349 KJ/mole is liberated. Which makes the reaction exothermic reaction.
- Size of an anion is always greater than the parent atom. As we see that during the formation of an anion one or more electrons are added to the atom. This extra addition of electrons increases the electron-electron repulsion in the valance shell of an atom which results in an extension of the electronic cloud. Due to an increase in some electrons in the outermost shell, the pull of nuclear on valance electron also Decreases. That’s why the size of an anion is always greater than the parent atom.
How does a cation Represent symbolically and what charge does it constitute?
It possesses a negative charge and the suffix (ide) is used for monoatomic anion and (ate) for the polyatomic anion. Such as hydride and hydrate.
Ionic bond and ionic compound:
As there is two type of charged ions one is a positively charged cation and the other is a negatively charged anion, due to their opposite polarity an electrostatic force of attraction arises between them. This electrostatic force worked as a driving force in the formation of an ionic bond. When two charges formed an ionic bond then a compound is formed which is named an ionic compound.
Classification of Ions:
Depending upon the type of atom from which an ion is formed we can classify it as a monoatomic, diatomic, or polyatomic ion.
Mono-atomic ion:
If an ion is formed from one type of atom it is referred to as a monoatomic ion. Examples of monoatomic cation and anion are;
- Aluminum cation is represented by the empirical formula Al?³.
- Proton is a commonly known caption of the hydrogen atom. This hydrogen caption is denoted by H ?¹
- Another example of a mono-atomic ion is manganese cation which is represented by the formula Mn ?². It also can form Mn ?³ and Mn ?4.
Illustration of monoatomic anion:
- Common example of a uni-negative ion is the fluoride ion which is represented by Fl ?¹.
- Along with this other examples are chloride ion, bromide ion, iodide ion, sulfide ion represented by chemical formula Cl?¹,
Br? ¹, I ?¹, S ?². As these belong to the 7th group, to complete their outermost shell they always prefer to gain an electron to form an anion.
Di-atomic ion:
If from two types of atoms an ion is made then it is referred to as a diatomic ion. An example of a diatomic ion is an Oxide ion denoted by the chemical formula O? ².
Polyatomic ion:
When an ion is made from more than one type of atom then it is referred to as a polyatomic or molecular ion.
Illustration of polyatomic cation:
Here below there are some common examples are provided;
- H3O? is the chemical formula of hydronium cation.
- Hg2?² is a mercurous cation.
- NH?4 is the chemical formula of ammonium cation.
Illustration of polyatomic anion
- A nitrate ion is a common example of a polyatomic anion. It is represented by the chemical formula NO3?.
- Cr2O3? is the chemical formula of chromium oxide anion.
- Another example of a polyatomic anion is the Sulfate ion which is represented by the chemical formula SO4?².
Ways one can create an ion;
There are several techniques one can use to create an ion. Here I explain two methods;
- Spontaneous collision
- Chemical interaction
Spontaneous collision:
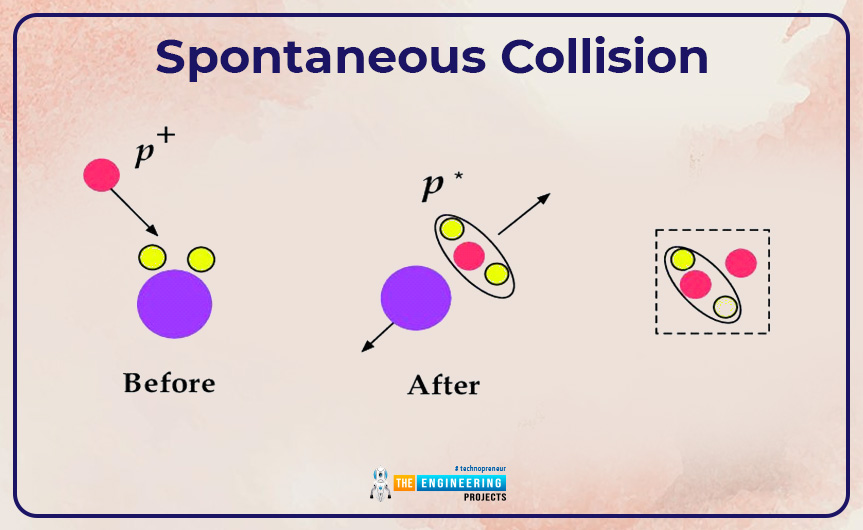
- We can create an ion from a spontaneous collision. Byword spontaneous means an event occurs without any apparent external cause. Collision is a process in which two bodies violently interact with each other. Through spontaneous collision among molecules of the liquid, an electron or group of electrons may be knocked off from an atom resulting in the formation of an ion. This ion is positively charged. Along with a positively charged ion, a free electron is also formed. This type of ionization is commonly named physical ionization. The free-electron that comes into the process during the collision may stick to itself or another atom resulting in the formation of a negatively charged ion.
Chemical interaction
- One can create an electron through another process which is commonly known as “ chemical interaction”. For example when we dissolve an ionic compound in any form of a solvent such as water. The atom that comprises salt undergoes the process of separation to form a negatively charged anion & positively charged cation. A common example one can see to understand this process is the dissolving of common salt (sodium chloride) in water. When sodium chloride is dissolved in water then NaCl disassociates into positive sodium cation and negative chlorine anion.
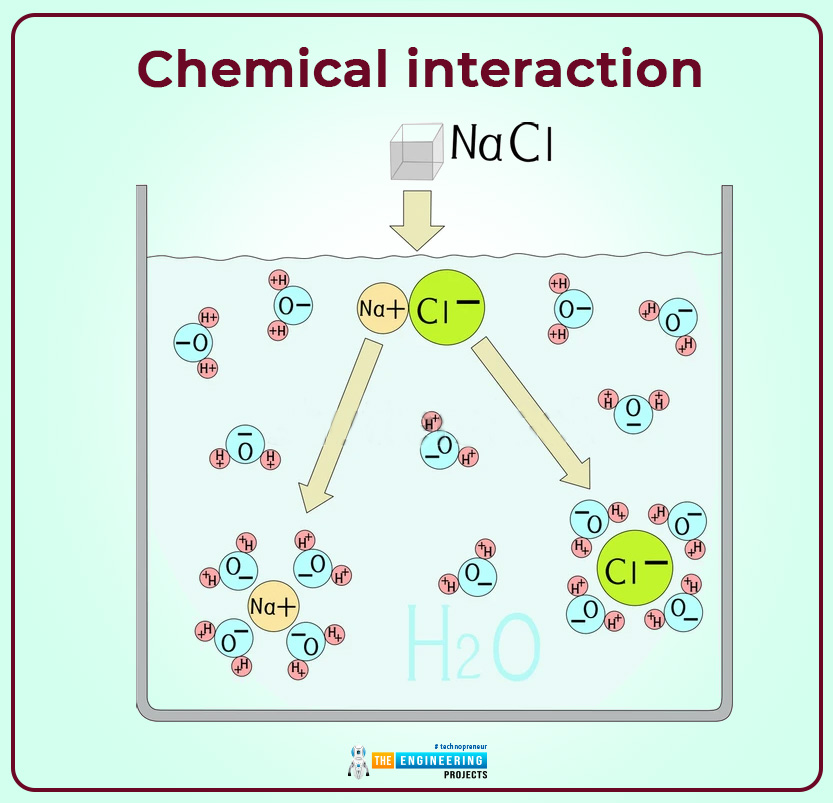
Here Na+ represent positive cation ionic specie. And Cl- represent anionic specie.
- Another process that can be carried out for the formation of ions is the passage of direct current from a dissolved solution which can conduct. As the current is passed through the solution the liquid molecules break and positive and negative ions are formed.
That’s All today. In this article, we learn about ion, its type, and the representation of charges on the ion. I try to explain aspects that make cation and anion quite different from each other. And in last we studied techniques which normally used to create an ion. I hope the given material for the term “Ion” is helpful for your academic requirement. If you have any queries regarding this article. Mention your question in the comment session. In the next tutorial, we will learn about molecular ions. Our platform tries its best to satisfy you. Keep tuned.



 Chemistry
Chemistry ahmedyasin
ahmedyasin 0 Comments
0 Comments

















